Pesticide Classification: Fungicide
Trade name: AdoMe 75% WG
Chemical group: Triazole + Oximinoaceta as a member of Strobilurin
Chemical composition: It is composed of two active ingredients against fungus
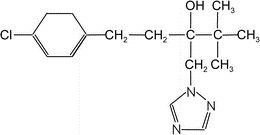
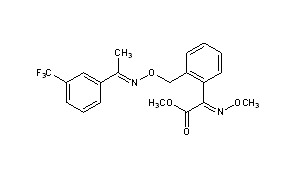
Tebuconazole + Trifloxystrobin
Mode of action:
AdoMe affects the fungi in two ways, as it destroys the cells of the plant pathogenic fungi through tebuconazole, which inhibits the synthesis of the sterol necessary for the formation of the cell walls of the fungi, and also AdoMe hinders the respiration in the mitochondria at cytochrome C through the trifloxystrobin.
Systemic action inside the plant:
Trifloxystrobin: a semi-systemic pesticide, which is transmitted through its transformation into steam and redistributed on the plant surface where it moves with water on the plant surface, and it also moves through the two surfaces of the Leaf.
Tebuconazole: a systemic pesticide, rapidly absorbed through the vegetative system, and translocate upward inside the plant with water movement through xylem.
AdoMe Efficacy:
Trifloxystrobin: It is mainly preventive fungicide, which control a broad-spectrum of Deuteromycota, Ascomycetes, Phycomycetes, and Basidiomycetes causing various plant diseases.
Tebuconazole: A preventive, curative and eradicative fungicide, which is also a broad- spectrum fungicide against fungal diseases such as (early blight, leaf spots, powdery mildew, smuts, rusts, white mold on onion and vegetables).
Diseases that are controlled by AdoMe: according to the recommendations of the pesticides committee of the Ministry of Agriculture and land reclamation with registration number 3390
| Crop | Disease | Application rate |
| Cucumber | Powdery mildew | 100 g / acre |
Recommendations of general usage:
A broad-spectrum fungicide against fungal diseases such as: (powdery mildew – early and late blight – spotting on potatoes, tomatoes, strawberries, grapes, mangoes, sugar beets and other crops).
| Crop | Disease | Application rate |
| Mango | Powdery mildew – Flower blight (Anthracnose) | 25 g / 100 L water |
| Grapes | Powdery mildew – Fruit rot | 25 g / 100 L water |
| Apples | Powdery mildew – Scab | 25 g / 100 L water |
| Peach – Apricot | Powdery mildew – Brown rot – Rusts – Shot-hole disease | 25 g / 100 L water |
| Cucurbits | Powdery mildew – Downy mildew –Gummy stem blight | 25 – 30 g /100 L water |
| Tomatoes – Pepper | Early blight – Powdery mildew | 25 – 30 g /100 L water |
| Onion – Garlic | Purple blotch – Downy mildew – White mold – Neck rot | 25 – 30 g /100 L water |
| Beans – Peas –Peanuts- Broad bean – Soybeans | Rusts – Leaf spots – Powdery mildew –White mold | 25 – 30 g /100 L water |
| Wheat – Barely | Rusts – Leaf spots | 120 g / acre |
Application precaution: Used as spray on the vegetative system.
PHI: 7 days.
Maximum residue limits of AdoMe in Cucumber (MRL):
| Pesticide | mg / kg Cucumber |
| Trifloxystrobin | 0.3 |
| Tebuconazole | 0.6 |
AdoMe advantages:
Trifloxystrobin: it cannot be washed by rain; also it is persisting for long period so it remains effective against fungal diseases for a long period after application.
Tebuconazole: a stable compound when exposed to heat and light, it does not hydrolyze in sterile pure water, and it takes more than a year to hydrolyze to half its concentration in a wide range of acidity (pH 4 – 9) at a temperature of 22 °C.
Mixability:
The pesticide can be mixed with fertilizers and pesticides, but after reviewing all the precautions for mixing and application, it is taken into account that it is a compound of two active ingredient, so it is not preferable to mix only with one compound at most when needed and after the study.





